Mastering Container Orchestration: A Deep Dive into Kubernetes
In the dynamic landscape of modern software development, containerization has become a game-changer, and at the forefront of this movement stands Kubernetes – an open-source container orchestration platform. In this article, we’ll embark on a journey to demystify Kubernetes and explore its pivotal role in managing and scaling containerized applications.
1. The Need for Container Orchestration
Containerization revolutionized application deployment by packaging applications and their dependencies into self-contained units, known as containers. However, as applications became more complex, managing these containers across different environments became challenging. This is where Kubernetes comes in.
1.1 What is Kubernetes?
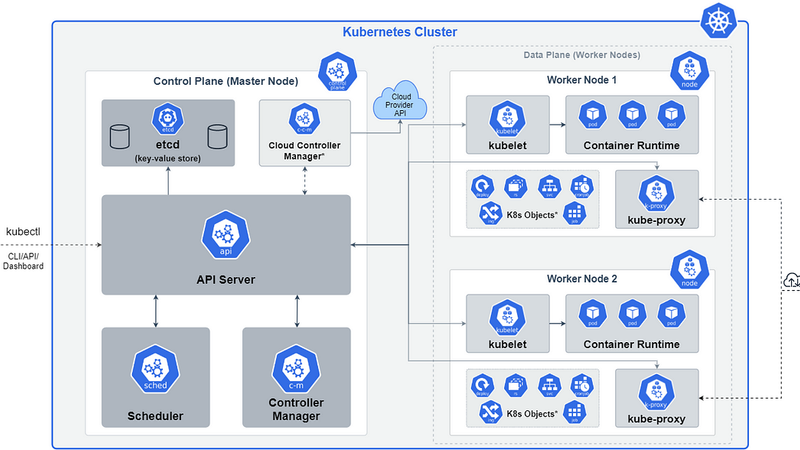
At its core, Kubernetes (often abbreviated as K8s) is a container orchestration tool that automates the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. Born from Google’s experience with managing large-scale applications, Kubernetes simplifies the complexity of managing containers at scale.
1.2 Key Concepts
-
Nodes: These are the individual machines (physical or virtual) that host containers. Nodes form the basis of a Kubernetes cluster.
-
Pods: The smallest deployable units in Kubernetes, pods can contain one or more containers that share storage and network resources. They ensure that related containers can communicate and work together efficiently.
-
Services: An abstraction that exposes a set of pods as a network service. Services enable load balancing and service discovery, allowing different parts of your application to communicate with each other.
-
ReplicaSets: A ReplicaSet ensures that a specified number of replicas of a pod are running at all times. It helps maintain the desired number of identical pods for reliability and availability.
-
Deployments: Deployments allow you to declaratively manage updates to your applications. They ensure that changes are applied with minimal disruptions and allow you to roll back if issues arise.
-
Namespaces: Kubernetes supports multiple virtual clusters backed by the same physical cluster. Namespaces provide a way to divide cluster resources among multiple users or teams.
2. Benefits of Kubernetes
2.1 Scalability and High Availability
Kubernetes enables automatic scaling of your applications based on CPU usage or custom metrics. It also ensures high availability by distributing pods across nodes and restarting failed containers.
2.2 Declarative Configuration
With Kubernetes, you describe the desired state of your application in YAML manifests. Kubernetes then works to make the current state match the desired state, simplifying configuration management.
2.3 Service Discovery and Load Balancing
Kubernetes offers built-in service discovery and load balancing, making it seamless to expose your services to the network and distribute traffic among pods.
3. Getting Started with Kubernetes
3.1 Installation and Setup
Setting up Kubernetes can be done on various cloud providers or even on local machines using tools like Minikube. For production environments, managed Kubernetes services like Amazon EKS, Google Kubernetes Engine, or Azure Kubernetes Service are recommended.
3.2 Deploying Applications
Deploying an application involves creating Kubernetes manifests, which define the desired resources and configurations. The kubectl command-line tool allows you to interact with the Kubernetes cluster and manage these resources.
3.3 Scaling and Updates
Kubernetes makes it easy to scale your application by adjusting the number of replicas or changing resource limits. Updates are managed by creating new ReplicaSets and gradually shifting traffic to them.
4. Challenges and Considerations
4.1 Learning Curve
Kubernetes’ power comes with a learning curve. Concepts like networking, security, and resource management can be complex for newcomers. However, various learning resources, online courses, and documentation are available to help bridge this gap.
4.2 Monitoring and Maintenance
As your cluster grows, monitoring and maintaining its health becomes crucial. Kubernetes offers integration with tools like Prometheus and Grafana for monitoring. Proper management of resources and configurations is essential to prevent performance bottlenecks and security vulnerabilities.
Conclusion
Kubernetes has transformed the way we build and deploy applications, enabling the efficient management of containerized workloads at scale. By understanding its fundamental concepts and embracing its capabilities, developers and DevOps engineers can harness the full potential of Kubernetes to drive innovation in the world of cloud-native applications.
As you embark on your journey with Kubernetes, remember that practice and hands-on experience are key. Explore its documentation, participate in the vibrant Kubernetes community, and witness how this orchestration marvel is shaping the future of modern software deployment. The world of container orchestration is evolving rapidly, and Kubernetes is leading the way.
Comments

About Blake Maxwell